44 why dont food labels list nucleic acids
Why is nucleic acid not on nutrition labels? - Toppr Virtually all food contains nucleic acids, so there is no purpose and no benefit from stating/labelling this fact on nutrition labels. Why Do We Need Fats, Carbohydrates, and Proteins in our Diet? Nucleic acids (like DNA) contain our genetic information, which are the blueprints from which proteins are made. The building blocks of proteins are called amino acids. There are 21 amino acids, but our body can only produce 12 of them. The other 9, named essential amino acids, must be ingested in order to make new proteins.
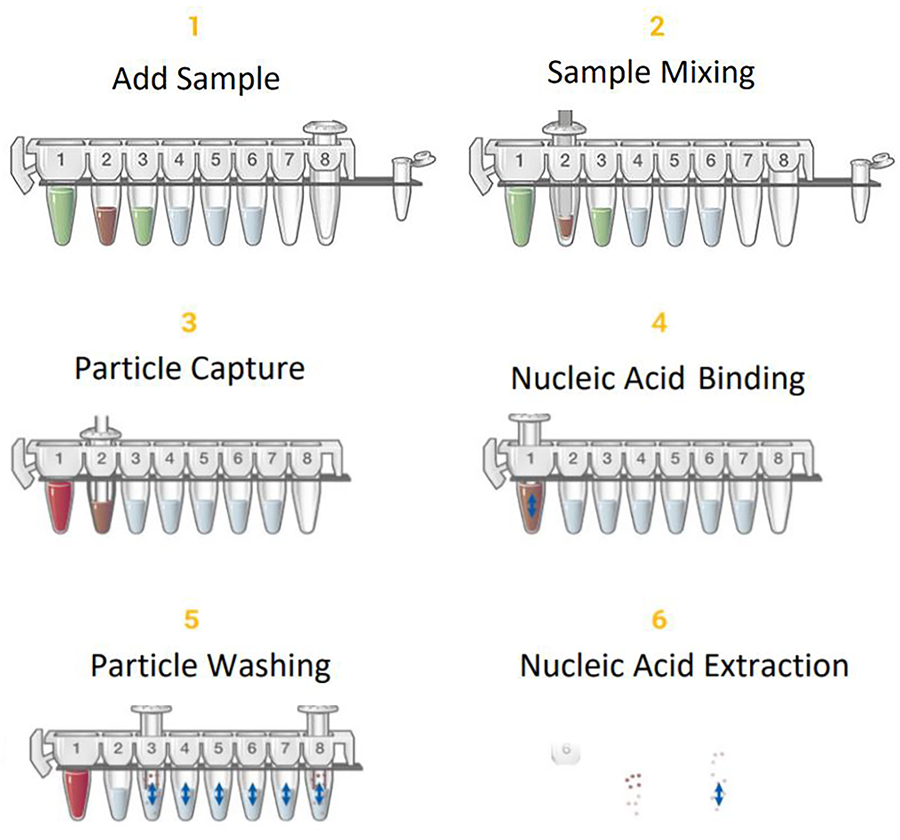
PDF Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids monomers DNA RNA 1. Label five five microcentrifuge tubes A-E respectively 2. Add 12 drops of unknown A to tube A, 12 drops of unknown B to tube B, 12 drops of unknown C to tube C, 12 drops of unknown D to tube D and 12 drops of unknown E to tube E. 3. Start with completing the test for the presence of nucleic acids (on the following page). 4.
Why dont food labels list nucleic acids
Guidance: Voluntary Labeling Food from Genetically Engineered Plants Modern biotechnology means the application of in vitro nucleic acid techniques, including recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and direct injection of nucleic acid into cells or organelles, or ... Nucleic Acid - Definition, Function and Examples - Biology Dictionary When our cells join nucleotides together to form the polymers called nucleic acids, it bonds them by replacing the oxygen molecule of the 3′ sugar of one nucleotide 's backbone with the oxygen molecule of another nucleotide's 5′ sugar. This is possible because the chemical properties of nucleotides allow 5′ carbons to bond to multiple phosphates. Foods That Contain Nucleic Acids | Healthy Living According to the Gordon Research Institute, these include increased bowel health and liver function. Some foods that contain nucleic acids include seafood, nuts, vegetables, mushrooms, yeast, beef,...
Why dont food labels list nucleic acids. DNA Isolation, Gel Electrophoresis, and PCR - Principles of Biology Isolation of Nucleic Acids. To study or manipulate nucleic acids, the DNA must first be extracted from cells. Various techniques are used to extract different types of DNA (Figure 2). Most nucleic acid extraction techniques involve steps to break open the cell, and then the use of enzymatic reactions to destroy all undesired macromolecules. Why do food labels not list nucleic acids? - Quora Both proteins and nucleic acids can bind with high specificity to a target molecule - antibodies bind other proteins, while siRNAs bind specific DNA sequences. Both proteins and nucleic acids can be catalysts - enzymes like phosphofructokinase are necessary for life. The ribosome uses a nucleic acid-based catalytic center to grow peptides. Why don't the Nutrition Facts statistics on food packages list the ... However, I can tell you that the pancreas secretes digestive enzymes that specifically break down consumed nucleic acids (DNAase & RNAase), just as it does for carbs, proteins & lipids. I'm not sure of the calorie content, though, if any. I suspect this may be a safety measure to degrade foreign nucleic acids from entering the body. 1 level 1 Nucleic Acids - Function, Examples, and Monomers - ThoughtCo Nucleic acids are macromolecules that store genetic information and enable protein production. Nucleic acids include DNA and RNA. These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group.
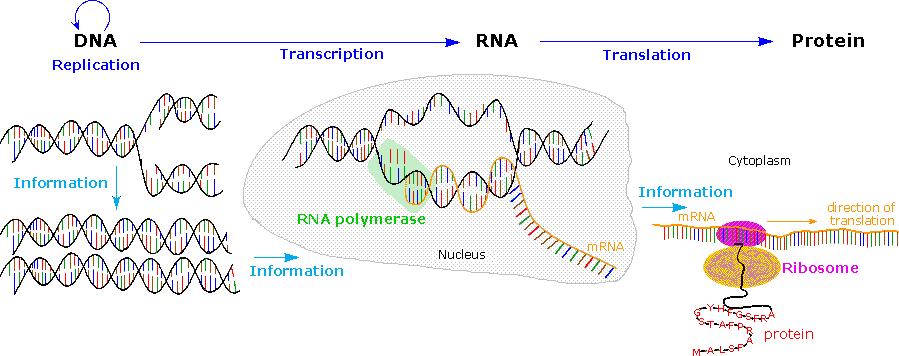
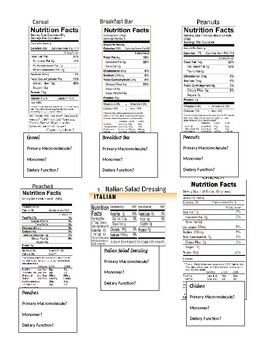
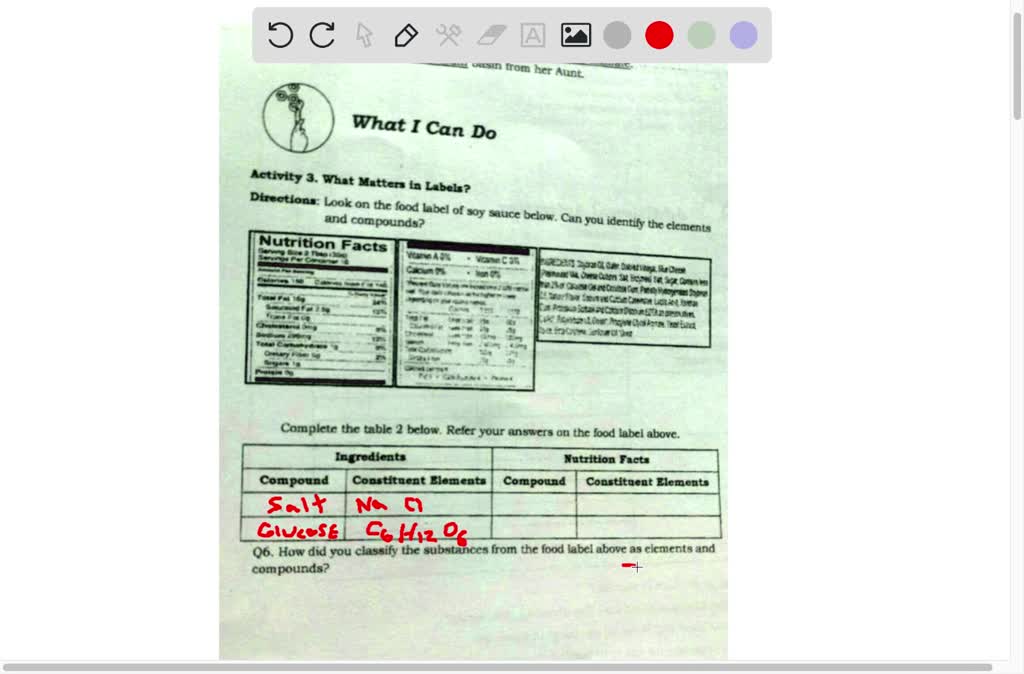
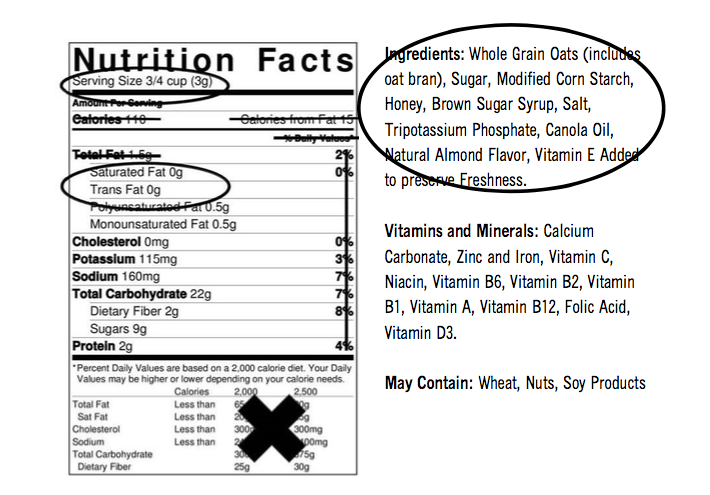
The Elements Of Nucleic Acids | Science Trends There are two different kinds of nucleic acid: ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is the form of nucleic acid common to all living things; all plants, animals, and even single-celled bacteria have DNA. RNA is used as the primary method of storing genetic material in some viruses, but scientists don't usually consider ... Why is nucleic acid not on nutrition labels? | Socratic Fruit, vegetables, meat, fish, poultry, nuts, beans, seeds, whole grains -- they are all made entirely of cells, with nucleic acids in all the nuclei of all their cells. It isn't meaningful to write this fact on nutrition labels because no animal or plant experiences a deficiency of nucleic acids. mmmmmmmmmm ――――――――― Food Label Analysis(1).docx - Food Label Analysis... - Course Hero Use your powerpoints to help you determine what the organic and inorganic compounds are in your food. List the 4 organic (Carbon-based) macromolecules found on the label. List inorganic molecules written on the label. Organic nutrients Inorganic (Minerals and Vitamins) Wheat Vitamin sugar A B Vitamin protein Vitamin B 6 Calcium Carbonate, Iron ... Nucleic Acids - Definition, Examples & Functions of Nucleic acids - BYJUS The Functions of Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are responsible for the transmission of inherent characters from parent to offspring. They are responsible for the synthesis of protein in our body DNA fingerprinting is a method used by forensic experts to determine paternity. It is also used for the identification of criminals.
All About Nucleic Acid Foods and Functions | livestrong The nucleic acid in foods is generally converted into uric acid and enters the blood and urine, where it can form crystals, a condition known as gout, according to September 2011 research in Seminars in Nephrology .. Eating more meat and seafood is associated with an increased risk of gout, whereas eating vegetable foods high in nucleic acid does not appear to have this effect. Nuclear Labeling | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US Nucleic acids are the obvious target for nuclear labeling Labeling the nucleus typically relies on some type of dye that binds nucleic acids, and depending on how much distinction you need between DNA and RNA and whether or not the cells you're labeling are live or fixed, your choice of stains will vary. Biological Polymers: Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids - ThoughtCo There are four basic kinds of biological macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These polymers are composed of different monomers and serve different functions. Carbohydrates: molecules composed of sugar monomers. They are necessary for energy storage. Why do food labels not list nucleic acids? - Quora No. Polynucleotidases are enzymes that break oligonucleotides into smaller oligonucleotides or single nucleotides. This occurs after the nucleic acid was cut ...
Why are Nucleic Acids Not on Nutrition Labels? 22 Oct 2021 — Nucleic acids are not on nutrition labels because they are not nutrients. They are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, which are used to ...
Junkfood Science: Processed foods aren't real food - Blogger There are plenty of natural health food and supplement vendors eagerly promoting incredible health benefits of lactic acid-fermented foods and supplements. Lactic bacteria have the most important role in fermented foods, according to Quest Health Library. Lactic acid fermented bacteria are behind "probiotic" foods that are all the rage today.
Why nucleic acid not in the food labels list? - Answers Unfortunately, the exact chemical formula for nucleic acids such as RNA and DNA is too long to list on this page. However, nucleic acids can be formulated as phosphoric acid and nucleosides in...
dna - Why aren't nucleic acids on Nutrition labels? - Biology Stack ... First, not all nitrogen in foods is found in proteins: it is also contained in variable quantities of other compounds, such as free amino acids, nucleotides, creatine and choline, where it is referred to as non-protein nitrogen (NPN). Only a small part of NPN is available for the synthesis of (non-essential) amino acids.
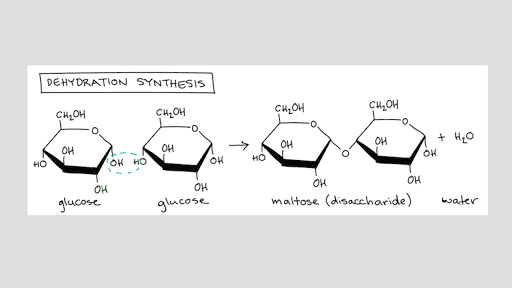
PPT Biological Molecules - WOU Nucleotides link together to form nucleic acids. The sugars bind to the phosphate groups to form the backbone of the chain. Before we begin, get out a piece of paper, put your name on it, and do the following: As review, sketch a diagram of an atom and label the particles.
Are natural foods and clean labels sustainable? - FoodNavigator And clean label, which is associated with an understandable ingredients list, is perceived by many as 'natural' and better for you. While the clean label movement continues to shape innovation in the food sector, FoodNavigator wants to put conventional wisdom to the test, asking whether clean label products are in fact healthier.
Changes to the Nutrition Facts Label | FDA - U.S. Food and Drug ... The Nutrition Facts label on packaged foods was updated in 2016 to reflect updated scientific information, including information about the link between diet and chronic diseases, such as obesity ...
Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats - Disorders of Nutrition - Merck ... Everyone needs 8 of these amino acids: isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. Infants also need a 9th one, histidine. The percentage of protein the body can use to synthesize essential amino acids varies from protein to protein.
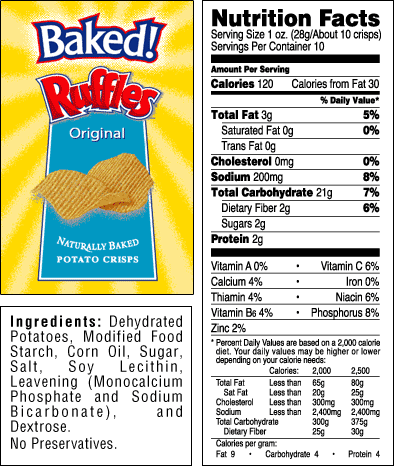
PDF Food Sources of Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins - Lane Community College PROTEINS provides amino acids for building muscles, hormones, enzymes, etc. No % DV on food labels SODIUM none, unless exercising a lot, then important for maintaining water balance outside cells may increase blood pressure in some people VITAMIN A : retinoids vision, outside & internal skin, bones VITAMIN A : carotenes in food
Nucleic Acid - Macromolecules 19 Aug 2015 — Although nucleic acids are an important macromolecule, they aren't on the food pyramid or on any nutrition label.
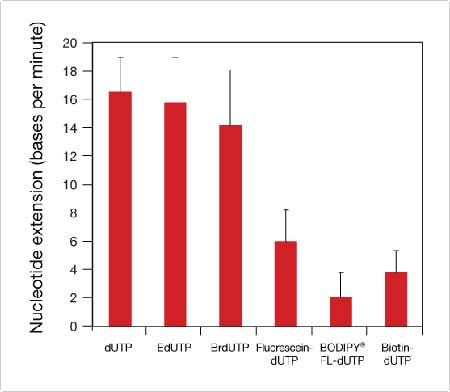
Overview of Protein Labeling | Thermo Fisher Scientific - US Biotinylation is the process of labeling proteins or nucleotides with biotin molecules and can be performed by enzymatic and chemical means. Chemical methods of biotinylation are most commonly used, and the biotinylation reagents used for this type of labeling share several basic features.
Lab 4 - Biologically important molecules Flashcards | Quizlet food labels list the amounts of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, but not nucleic acids. Why Not? nucleic acids do not supply the body with energy - our cells can make their own nucleic acids therefore they don't need to be put onto food labels. what was our unknown. protein. Recommended textbook solutions. Anatomy and Physiology
Food Labels: Fat & Cholesterol | Home & Garden Information Center Limit these sources of unhealthy fat and cholesterol in the list of ingredients: animal fat (beef, ham, pork, bacon, lamb, chicken, turkey), lard, hardened fat or oil, egg and egg-yolk solids, cream, butter, whole-milk solids, palm oil, palm kernel oil, hydrogenated vegetable oil, vegetable shortening, coconut, coconut oil, and cocoa butter.
What Are The Monomers Of Lipids? | Science Trends Nucleotides are the blueprint or basis of construction for amino acids, storing the information needed to create them. Nucleotides are the monomers created from nucleic acids such as ribonucleic acid or RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. RNA and DNA both hold an organism's genetic code, and the nucleotide monomers are constructed out of a nitrogenous base, a phosphate, and a five-carbon ...
Foods That Contain Nucleic Acids | Healthy Living According to the Gordon Research Institute, these include increased bowel health and liver function. Some foods that contain nucleic acids include seafood, nuts, vegetables, mushrooms, yeast, beef,...

Chlorella Tablets Mega-Pack 1000 Tablets Cracked Cell, Raw, Non-GMO. 100% Pure Chlorella Pyrensoidosa. Green Superfood. High Protein, Chlorophyll & ...
Nucleic Acid - Definition, Function and Examples - Biology Dictionary When our cells join nucleotides together to form the polymers called nucleic acids, it bonds them by replacing the oxygen molecule of the 3′ sugar of one nucleotide 's backbone with the oxygen molecule of another nucleotide's 5′ sugar. This is possible because the chemical properties of nucleotides allow 5′ carbons to bond to multiple phosphates.
Guidance: Voluntary Labeling Food from Genetically Engineered Plants Modern biotechnology means the application of in vitro nucleic acid techniques, including recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and direct injection of nucleic acid into cells or organelles, or ...




























Post a Comment for "44 why dont food labels list nucleic acids"